Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction to Nursing Student Clinicals
Picture this: it’s 5:30 AM, and you’re standing outside a hospital in crisp scrubs, heart racing, wondering if you’re truly ready for what lies ahead. For thousands of nursing students, this moment marks the beginning of their most transformative educational experience—nursing student clinicals. These hands-on rotations bridge the gap between textbook theory and real-world patient care, serving as the proving ground where future nurses are truly born. While student research shows that clinical experiences significantly impact career readiness, many nursing students feel underprepared for their first day on the floor. Additional student research reveals that those who approach nursing student clinicals with strategic preparation consistently outperform their peers in both competence and confidence.
What Are Clinical Rotations and Why They Matter (Strategy #1: Understanding Your Clinical Foundation)
Nursing student clinicals are supervised, hands-on training experiences where students apply classroom knowledge in real healthcare settings. These rotations typically span hospitals, clinics, long-term care facilities, and community health centers, exposing students to diverse patient populations and medical conditions.
Why Clinical Rotations Matter:
- Real-world skill application – Transform theoretical knowledge into practical nursing competencies
- Patient interaction experience – Develop therapeutic communication and bedside manner
- Critical thinking development – Learn to make quick, evidence-based clinical decisions
- Professional identity formation – Transition from student to confident healthcare professional
- Career pathway exploration – Discover specialty areas that align with your interests and strengths
- Networking opportunities – Build relationships with potential employers and mentors
- Confidence building – Gain competence through repetitive practice in safe environments
Overview of What This Guide Covers
This comprehensive guide presents nine essential strategies designed to help you excel throughout your nursing student clinicals. You’ll discover practical preparation techniques, learn how to maximize every learning opportunity, and develop skills to overcome common challenges. By the end, you’ll have a clear roadmap for transforming clinical rotations from anxiety-inducing experiences into career-defining opportunities.
How to Prepare for Your First Clinical Experience (Strategy #2 & #3)
Success in nursing student clinicals begins long before you step onto the hospital floor. Proper preparation sets the foundation for confident, competent practice and helps you avoid preventable stress. The following strategies ensure you’re physically, administratively, and mentally ready to make the most of every clinical day.
Essential Documentation and Requirements (Strategy #2: Completing Pre-Clinical Requirements)
Before starting clinical rotations, you must complete extensive documentation to protect both patients and yourself. Begin this process at least 4-6 weeks before your scheduled start date.
- Health records and immunizations – Submit proof of required vaccinations including hepatitis B series, MMR, varicella, Tdap, and annual flu shots; include negative TB test results or chest X-ray documentation
- Background checks and certifications – Complete criminal background checks, obtain Basic Life Support (BLS) certification through the American Heart Association, and secure any state-specific clearances
- Clinical site-specific paperwork – Review and sign confidentiality agreements, HIPAA compliance forms, infection control policies, and emergency contact information
- Drug screening – Undergo pre-clinical drug testing as required by most healthcare facilities
- Liability insurance – Obtain student malpractice insurance, often provided through your nursing program
- Physical examination documentation – Provide recent physical exam results confirming your ability to perform clinical duties
What to Pack in Your Clinical Bag (Strategy #3: Organizing Your Clinical Essentials)

A well-organized clinical bag prevents forgotten items and demonstrates professionalism. Pack your bag the night before each clinical day.
- Required supplies and equipment – Stethoscope with name tag, penlight, bandage scissors, permanent marker, clipboard or portable notebook, watch with second hand, pen (black or blue ink)
- Organizational tools – Clinical reference cards (lab values, medication guidelines, assessment checklists), pocket-sized medical dictionary or nursing guide, small notebook for taking patient notes, medication calculation reference card
- Comfort items for long shifts – Healthy snacks that don’t require refrigeration, refillable water bottle, breath mints or gum, extra hair ties, deodorant, blister prevention bandages, phone charger with portable battery
Professional Attire Guidelines
Your appearance communicates respect for patients, staff, and the nursing profession itself.
- Scrubs and uniform requirements – Wear clean, wrinkle-free scrubs in colors specified by your program; ensure scrubs fit appropriately—not too tight or too loose; avoid scrubs with excessive pockets that could harbor bacteria
- Appropriate footwear – Choose closed-toe, non-slip shoes with adequate arch support; select shoes that are easy to clean and can withstand bodily fluids; break in new shoes before wearing them to clinicals
- Accessories and personal presentation – Keep jewelry minimal—small stud earrings and one simple ring maximum; maintain short, clean fingernails with no polish or only clear polish; tie long hair back away from face; avoid strong perfumes, colognes, or scented lotions; ensure visible tattoos comply with facility policies
Ways to Maximize Learning During Clinical Rotations (Strategy #4, #5 & #6)
The quality of your nursing student clinicals depends not just on showing up, but on actively engaging with every learning opportunity. These strategies help you extract maximum value from each clinical experience, transforming routine tasks into building blocks for your nursing career.
Steps to Building Strong Relationships with Preceptors (Strategy #4: Connecting with Clinical Mentors)
Your clinical preceptor or instructor serves as your guide, evaluator, and advocate. A positive relationship with this mentor significantly enhances your learning experience.
- Communication strategies – Arrive early to discuss the day’s goals and patient assignments; ask for feedback regularly rather than waiting for formal evaluations; communicate honestly about your comfort level with procedures; express gratitude for teaching moments and constructive criticism
- Asking meaningful questions – Prepare questions before clinical days based on upcoming patient conditions; ask “why” questions that deepen understanding beyond “how”; request rationale behind clinical decisions and interventions; inquire about alternative approaches to patient care situations
- Demonstrating initiative and reliability – Volunteer for new experiences even when they seem challenging; complete assignments thoroughly and by deadlines; offer assistance to staff nurses and fellow students; follow through on commitments and arrive punctually every clinical day; take detailed notes and review them before the next session
How to Develop Hands-On Clinical Skills (Strategy #5: Mastering Clinical Procedures)
Technical proficiency develops through repeated practice under supervision. Approach skill development systematically during nursing student clinicals.
- Volunteering for procedures – Raise your hand immediately when opportunities arise for catheter insertions, IV starts, wound care, or medication administration; shadow experienced nurses during complex procedures you’re not yet cleared to perform independently; request to observe specialized procedures in operating rooms or procedural areas
- Practicing assessments – Conduct complete head-to-toe assessments on every assigned patient; compare your findings with your preceptor’s assessment; practice specific assessment techniques like heart and lung auscultation on multiple patients; document your findings promptly and accurately
- Documentation practice – Review charts to understand documentation standards; practice writing nursing notes using SBAR or DAR formats; learn to document efficiently without sacrificing thoroughness; ask preceptors to review your documentation before finalizing
Struggling with complex nursing assignments? StudentResearch.net connects you with degree-holding professionals who possess advanced qualifications in nursing and healthcare fields. Our expert writers deliver academically rigorous papers that demonstrate deep subject matter expertise, helping you achieve excellence in your coursework.
Ways to Connect Theory to Practice
Bridging the gap between classroom learning and clinical application strengthens your clinical reasoning abilities.
- Applying classroom knowledge – Review pathophysiology related to your patients’ diagnoses before clinical days; reference pharmacology notes when administering medications; apply nursing theories to patient care planning
- Understanding the “why” behind interventions – Question the rationale for every medication, procedure, and nursing intervention; research evidence-based practices supporting the care you observe; discuss with preceptors how interventions connect to patient outcomes
Time Management Strategies for Clinical Success (Strategy #6: Managing Your Clinical Schedule)
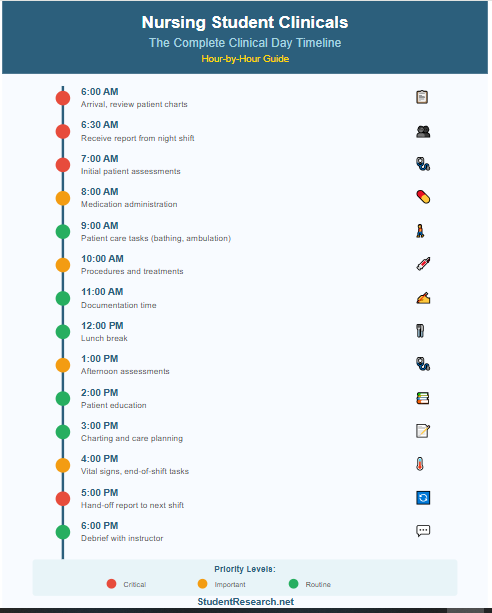
Effective time management prevents overwhelm and ensures safe, thorough patient care during nursing student clinicals.
- Creating patient care schedules – Organize morning tasks by priority—assessments, medication administration, treatments; build in buffer time for unexpected situations; plan documentation time after completing procedures
- Prioritizing tasks effectively – Use the ABC priority framework—Airway, Breathing, Circulation issues first; address safety concerns immediately; delegate appropriate tasks when working with nursing assistants; recognize which tasks can be batched together efficiently
- Balancing multiple responsibilities – Develop a systematic routine for checking on each patient; set phone alarms for time-sensitive medications or assessments; communicate with team members about your workload; ask for help before falling behind
How to Overcome Common Clinical Challenges (Strategy #7 & #8)
Even well-prepared nursing students encounter obstacles during clinical rotations. Anticipating common challenges and developing coping strategies ensures these difficulties become learning opportunities rather than roadblocks.
Ways to Manage Clinical Anxiety and Stress (Strategy #7: Conquering Clinical Nerves)
Clinical anxiety affects nearly every nursing student at some point. Recognizing and addressing these feelings promotes both your wellbeing and patient safety.
- Pre-clinical jitters – Practice deep breathing exercises before entering the facility; arrive early to settle in and review the day’s plan; remind yourself that mistakes are part of learning; connect with supportive classmates who understand your experiences; maintain perspective—clinical anxiety typically decreases significantly after the first few weeks
- Coping mechanisms for high-pressure situations – Step away briefly to regroup when feeling overwhelmed; use positive self-talk to counter negative thoughts; Focus on one task at a time rather than everything at once; debrief difficult situations with your instructor or trusted mentor; maintain work-life balance through adequate sleep, nutrition, and exercise
- Building confidence over time – Keep a success journal documenting skills mastered and positive feedback received; acknowledge small victories and progressive improvements; reflect on how much you’ve grown since your first clinical day; remind yourself that every expert nurse was once a nervous student
How to Handle Difficult Patient Interactions (Strategy #8: Navigating Complex Patient Care)
Not every patient interaction flows smoothly. Developing skills for challenging situations protects both patient relationships and your professional composure.
- Communication with diverse populations – Learn basic phrases in languages common in your clinical area; use teach-back methods to confirm patient understanding; adapt communication style to patient age, cognitive ability, and cultural background; utilize hospital interpreter services rather than relying on family members; demonstrate cultural humility by acknowledging your knowledge limitations
- De-escalation techniques – Remain calm and speak in a steady, reassuring tone; Maintain appropriate distance and non-threatening body language; listen actively to patient concerns without interrupting; validate emotions while setting boundaries on unacceptable behavior; remove potential triggers from the environment when possible
- Setting professional boundaries – Politely redirect conversations that become too personal; decline patient requests that fall outside your scope of practice; inform preceptors immediately about inappropriate patient behavior; remember that you’re not required to tolerate verbal abuse or harassment
Learning from Clinical Mistakes
Errors during nursing student clinicals, while stressful, provide invaluable learning experiences when handled appropriately.
- Viewing errors as growth opportunities – Acknowledge mistakes promptly and honestly; analyze what contributed to the error and how to prevent recurrence; seek additional practice with skills where mistakes occurred; remember that making errors in supervised settings prepares you to avoid them in independent practice
- Reporting and addressing concerns appropriately – Follow facility protocols for reporting medication errors or safety concerns; notify your preceptor immediately when mistakes occur; participate fully in error analysis discussions; accept feedback graciously and implement suggested improvements
Need help maintaining academic integrity while managing clinicals? StudentResearch.net guarantees 100% original content created from scratch for every assignment. We provide comprehensive plagiarism reports with each paper, ensuring your work meets the highest academic standards. Your success is our commitment.
Ways to Build Professional Development Through Clinicals (Strategy #9)
Nursing student clinicals offer more than just skill development—they provide a launching pad for your nursing career. Strategic networking and professional growth activities during clinicals create opportunities that extend far beyond graduation.
Networking Strategies and Career Exploration (Strategy #9: Leveraging Clinicals for Your Career)
The connections you build during clinical rotations often lead directly to job offers and career advancement.
- Building relationships with nursing staff – Introduce yourself professionally to staff nurses and managers; ask experienced nurses about their career paths and specialty choices; exchange contact information with nurses who inspire you; send thank-you notes or emails after particularly valuable learning experiences; maintain connections through professional social media platforms like LinkedIn
- Identifying specialty interests – Reflect on which clinical rotations energized versus drained you; consider patient populations you felt most passionate about serving; notice which nursing tasks you found most engaging; discuss specialty options with nurses working in areas that interest you; seek additional clinical hours or shadowing opportunities in specialties under consideration
- Creating future job opportunities – Express interest in employment to nurse managers during strong clinical rotations; inquire about new graduate residency programs at facilities where you’re completing clinicals; demonstrate reliability, competence, and positive attitude consistently; volunteer for additional shifts or learning opportunities when available
How to Develop Critical Thinking Skills in Clinical Settings
Critical thinking separates competent nurses from exceptional ones. Nursing student clinicals provide the perfect environment to strengthen this essential skill.
- Clinical reasoning in real-time – Practice anticipating potential complications for each patient; ask yourself “what if” questions about possible scenario changes; Think through the cascade effects of interventions before implementing them; discuss your clinical reasoning process with preceptors for feedback
- Evidence-based decision making – Research current best practices for patient conditions you encounter; compare textbook recommendations with actual clinical practice; Question outdated traditions that lack evidence-based support; Learn to access and evaluate research literature quickly
- Reflective practice techniques – Journal about significant clinical experiences after each shift; Identify moments where you’d handle situations differently; Celebrate instances of excellent clinical judgment; Set specific goals for improvement based on reflections
Conclusion: Steps to Clinical Success
Nursing student clinicals can be challenging, but they represent the most transformative phase of your nursing education. When you master these 9 essential strategies—from thorough preparation to active learning engagement to professional networking—you’ll excel in clinical rotations and build confidence as a future nurse. The skills you develop during nursing student clinicals extend far beyond technical proficiency; they shape your professional identity, clinical judgment, and commitment to patient-centered care.
Key Takeaways for Thriving in Nursing Student Clinicals
Remember that every expert nurse you admire once stood exactly where you are now, feeling nervous before their first clinical day. The difference between nurses who merely survive clinicals and those who thrive lies in their approach—preparedness, intentionality, and willingness to embrace both successes and setbacks as learning opportunities. As you implement these nine strategies throughout your clinical experiences, you’ll notice your confidence growing, your skills sharpening, and your passion for nursing deepening. Take the first step today by reviewing your clinical requirements, organizing your supplies, and committing to active engagement during every clinical shift. Your journey from nervous student to competent nurse begins now—embrace it fully.
Juggling clinical rotations and assignments across time zones? StudentResearch.net offers round-the-clock customer support for consultations, revisions, and urgent assistance whenever you need it. Our international team ensures you’re never alone in your academic journey, regardless of your schedule or location.