Table of Contents
ToggleThe transition from classroom theory to hands-on clinical practice represents one of the most challenging yet rewarding phases of nursing education. Understanding clear objectives for clinical nursing students is fundamental to building confidence, competence, and professional excellence in patient care settings.
Clinical objectives serve as your roadmap through hospital wards, patient interactions, and technical procedures. They help you measure progress, identify areas for improvement, and prepare for professional nursing responsibilities. This comprehensive guide explores seven essential objectives every clinical nursing student should master, covering patient assessment, medication safety, professional communication, and evidence-based practice. By focusing on these core competencies, you’ll develop the knowledge, skills, and clinical judgment necessary to provide exceptional patient care.
What Are Core Clinical Competencies and Why They Matter
Core clinical competencies are the essential knowledge, skills, and attitudes that nursing students must develop to provide safe, effective patient care. These foundational abilities integrate theoretical knowledge with practical application, preparing students for real-world healthcare environments.
Why core competencies matter:
- Ensure patient safety and quality care delivery
- Build confidence in clinical decision-making
- Meet professional nursing standards and regulatory requirements
- Prepare students for licensure examinations and employment
- Foster critical thinking and problem-solving abilities
- Enable seamless transition from student to professional nurse
Patient Assessment Skills: How to Conduct Comprehensive Evaluations
Objective #1: Master Patient Assessment and Critical Thinking
Patient assessment forms the foundation of quality nursing care. Developing systematic evaluation skills allows you to identify patient needs, detect changes in condition, and make informed clinical decisions.
Steps to Performing Head-to-Toe Assessments
Conduct assessments in a logical sequence: begin with general appearance and vital signs, then progress through body systems from head to toe. Use inspection, palpation, percussion, and auscultation techniques. Document findings immediately, noting normal and abnormal observations. Practice consistency to develop speed and accuracy over time.
How to Develop Clinical Reasoning Abilities
Clinical reasoning develops through deliberate practice and reflection. Analyze patient data systematically, identify patterns, consider differential diagnoses, and anticipate potential complications. Seek feedback from preceptors, participate in case study discussions, and reflect on clinical experiences to strengthen your analytical thinking.
Safe Medication Administration: What Nursing Students Must Know
Objective #2: Ensure Safe Medication Practices
Medication errors represent a leading cause of patient harm. Mastering safe administration practices protects patients and builds your professional credibility.
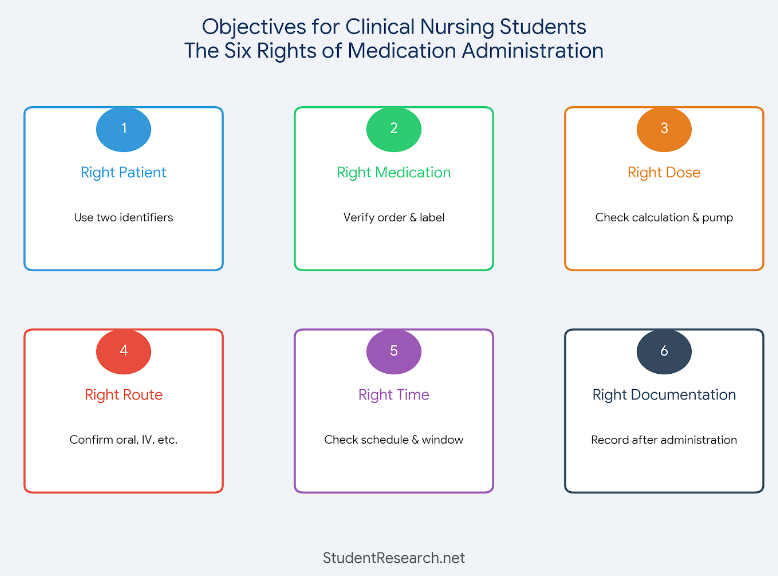
Understanding the Six Rights of Medication Administration
Always verify: right patient (using two identifiers), right medication, right dose, right route, right time, and right documentation. Never skip verification steps, even under time pressure. Question any orders that seem unusual or unclear before administering.
Ways to Prevent Medication Errors in Clinical Settings
- Double-check high-alert medications with another nurse
- Avoid distractions during medication preparation
- Use bar-code scanning technology correctly
- Stay current on medication knowledge and drug interactions
- Report near-misses to improve system safety
Types of Documentation and Communication Standards
Objective #3: Master Professional Communication
Effective documentation and communication are essential for patient safety and legal protection. Understanding different types ensures comprehensive care coordination.
Key documentation and communication standards include:
- Narrative nursing notes documenting patient status and interventions
- Flow sheets tracking vital signs, intake/output, and routine care
- Admission and discharge summaries capturing patient journey
- Incident reports for adverse events and safety concerns
- Progress notes reflecting patient response to treatment
- SBAR format for structured verbal handoffs and reports
- Interdisciplinary care plans coordinating team-based care
How to Use Electronic Health Record (EHR) Systems
Familiarize yourself with your facility’s EHR platform early. Document accurately, objectively, and promptly using approved abbreviations. Include assessment findings, interventions performed, patient responses, and teaching provided. Never chart procedures before completion or document for others.
Communicating Effectively with Interdisciplinary Teams
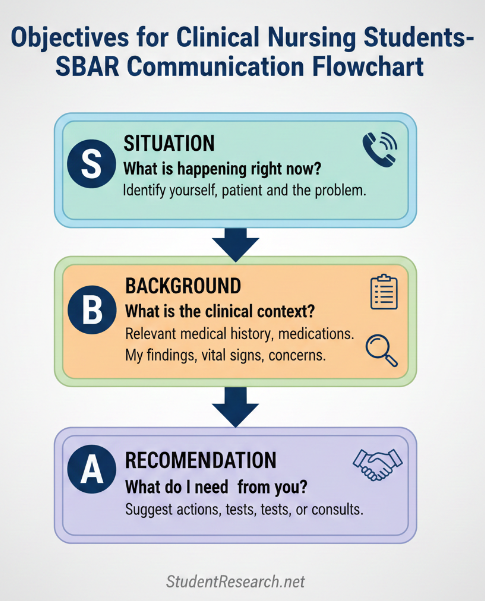
Use SBAR (Situation, Background, Assessment, Recommendation) format for structured communication. Speak clearly and confidently, especially when reporting critical changes. Listen actively to other team members, ask clarifying questions, and respect diverse professional perspectives to enhance collaborative patient care.
How to Develop Professional Skills and Patient-Centered Care
Beyond technical abilities, nursing excellence requires interpersonal skills, time management, and commitment to evidence-based practice. These professional competencies distinguish competent nurses from exceptional ones.
Building Therapeutic Nurse-Patient Relationships: A Guide
Objective #4: Establish Patient Trust and Rapport
Therapeutic relationships form the cornerstone of quality nursing care, promoting healing and patient cooperation.
How to Practice Active Listening and Empathy
- Maintain appropriate eye contact and open body language
- Allow patients to express concerns without interruption
- Reflect back what you hear to confirm understanding
- Validate patient feelings and experiences
- Show genuine interest in the patient as a whole person
- Use therapeutic silence to encourage deeper sharing
Understanding Cultural Diversity in Patient Care
- Recognize your own cultural biases and assumptions
- Learn about diverse health beliefs and practices
- Use professional interpreters for language barriers
- Respect religious practices and dietary restrictions
- Adapt care plans to align with cultural preferences
- Ask patients about their cultural needs rather than assuming
Time Management Strategies: How Clinical Nursing Students Prioritize Tasks
Objective #5: Master Clinical Time Management
Effective time management prevents burnout, reduces errors, and ensures all patients receive timely care.
Ways to Organize Multiple Patient Assignments
- Review patient charts and prioritize based on acuity at shift start
- Cluster care activities to minimize interruptions
- Delegate appropriate tasks to nursing assistants
- Use organizational tools like brain sheets or checklists
- Anticipate patient needs and gather supplies in advance
- Build buffer time for unexpected situations
How to Respond to Emergency Situations with Confidence
- Know your facility’s rapid response protocols
- Stay calm and call for help immediately
- Perform systematic ABCs assessment (Airway, Breathing, Circulation)
- Initiate basic life support measures while waiting for assistance
- Document critical events thoroughly after stabilization
- Debrief with team members to learn from experience
What Is Evidence-Based Practice and Why It’s Essential
Evidence-based practice integrates current research, clinical expertise, and patient preferences to optimize outcomes and advance nursing science.
How to Apply Current Research to Patient Care
- Stay current by reading nursing journals and attending conferences
- Question traditional practices that lack research support
- Collaborate with nurse researchers and educators
- Use clinical databases to search for best practice guidelines
- Implement research findings within your scope of practice
- Share evidence-based knowledge with colleagues
Examples of Quality Improvement Initiatives
- Reducing catheter-associated urinary tract infections through protocols
- Implementing fall prevention programs with hourly rounding
- Improving hand hygiene compliance through education campaigns
- Decreasing medication errors via double-check systems
- Enhancing patient satisfaction through bedside shift reports
- Monitoring pressure ulcer rates and prevention strategies
“See Quality Before You Commit!”
Explore StudentResearch.net’s extensive portfolio of sample nursing papers, case studies, and research projects. Browse real examples showcasing our expert writing quality and academic standards. Make confident, informed decisions about your academic support with free previews available now.
Essential Technical Skills: What Procedures Nursing Students Must Master
Technical proficiency builds confidence and ensures patient safety during hands-on care. Mastering fundamental procedures prepares you for diverse clinical settings.
Types of Nursing Procedures and Interventions
Objective #6: Perform Core Clinical Procedures
Competency in essential procedures distinguishes prepared nursing students from those still developing foundational skills.
How to Perform Wound Care and Sterile Techniques
- Assess wound characteristics: size, depth, drainage, and tissue type
- Maintain sterile field using proper hand hygiene and barrier precautions
- Select appropriate dressings based on wound stage and drainage
- Use clean-to-dirty technique during wound cleaning
- Document wound measurements and healing progress with photos when possible
- Recognize signs of infection requiring immediate intervention
Steps to Managing IV Therapy and Catheterization
- Verify orders and assess patient for contraindications
- Select appropriate equipment and prepare supplies before procedure
- Use smallest gauge catheter appropriate for therapy
- Follow strict aseptic technique during insertion
- Secure catheters properly and monitor insertion sites regularly
- Recognize complications like infiltration, phlebitis, or infection early
Monitoring Vital Signs: How to Recognize Abnormalities
Accurate vital sign measurement and interpretation enables early detection of patient deterioration and guides clinical interventions.
How to Identify Early Warning Signs of Patient Deterioration
- Recognize subtle changes: restlessness, confusion, or decreased responsiveness
- Note trending patterns rather than isolated values
- Use early warning scoring systems when available
- Trust your clinical intuition when something seems wrong
- Escalate concerns promptly to senior nurses or physicians
- Document all assessment findings and interventions clearly
Ways to Use Medical Equipment Accurately
- Complete competency training before using new equipment
- Perform equipment checks at beginning of every shift
- Follow manufacturer guidelines for calibration and maintenance
- Apply correct technique for blood pressure, oxygen saturation, and temperature
- Troubleshoot common equipment issues before calling for assistance
- Report malfunctioning equipment immediately to prevent errors
Infection Control Protocols: What Every Nursing Student Should Know
Objective #7: Implement Safety and Infection Control
Infection prevention protects both patients and healthcare workers while reducing healthcare costs and complications.
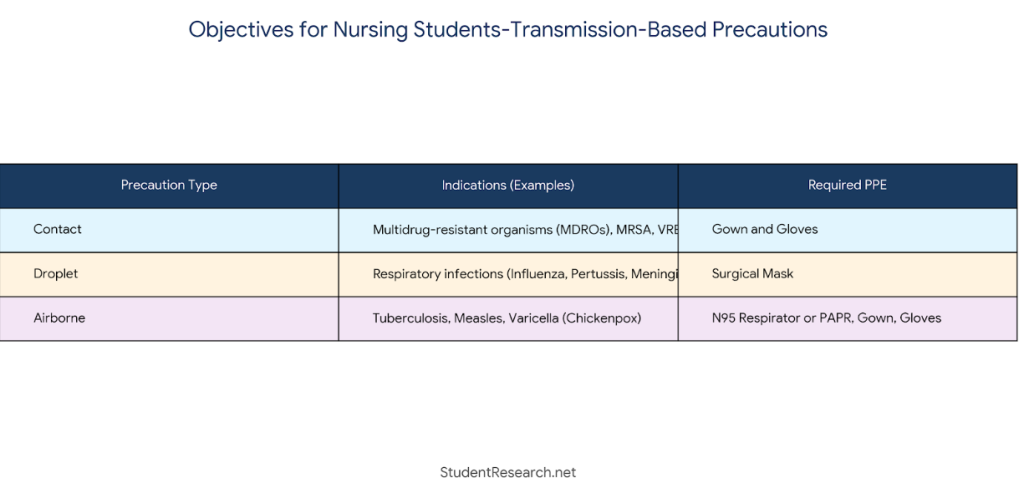
Understanding Standard and Transmission-Based Precautions
- Apply standard precautions with every patient contact
- Use personal protective equipment (PPE) appropriate to risk level
- Implement contact precautions for multidrug-resistant organisms
- Follow droplet precautions for respiratory infections
- Use airborne precautions for tuberculosis and other airborne diseases
- Properly don and doff PPE in correct sequence
How to Prevent Healthcare-Associated Infections (HAIs)
- Practice rigorous hand hygiene before and after patient contact
- Maintain sterile technique during invasive procedures
- Remove unnecessary catheters and lines promptly
- Implement ventilator-associated pneumonia prevention bundles
- Educate patients and families about infection prevention
- Participate in infection surveillance and reporting systems
Conclusion
Mastering these seven essential objectives for clinical nursing students—patient assessment, medication safety, professional communication, therapeutic relationships, time management, technical procedures, and infection control—provides the foundation for nursing excellence. Each objective builds upon the others, creating a comprehensive skill set that prepares you for the challenges and rewards of professional practice. Remember that clinical competency develops progressively through deliberate practice, reflection, and continuous learning. Embrace every clinical opportunity as a chance to strengthen these core competencies, seek feedback from experienced nurses, and commit to lifelong professional development. Your dedication to these objectives today will shape the exceptional nurse you become tomorrow.
“Struggling with Nursing Citations and Formatting?“
StudentResearch.net offers free academic resources designed for nursing students: APA citation guides, research writing tips, literature review templates, and evidence-based practice tutorials. Access expert educational support that strengthens your writing skills—whether you need guidance or full academic assistance.