Table of Contents
ToggleWhy is Nursing in Switzerland Important for Your Future?
Switzerland’s healthcare system offers an exceptional pathway for international students pursuing nursing careers in Europe’s most prestigious medical environment. Recent student research reveals that nursing in Switzerland for international students delivers world-class education combined with guaranteed employment upon graduation. The country urgently needs qualified healthcare professionals, creating unprecedented opportunities in this high-demand field. Swiss hospitals provide competitive salaries, excellent working conditions, and a commitment to patient care excellence that sets global standards. This golden opportunity allows ambitious learners to build stable, high-paying careers in one of the world’s most respected healthcare systems.
Why is Nursing in Switzerland Important for Your Future
- Global Recognition: Swiss nursing degrees earn worldwide respect and open international career doors
- High Earning Potential: Starting salaries range from CHF 60,000 to CHF 80,000 annually
- Job Security: Healthcare worker shortage guarantees employment upon graduation
- Quality of Life: Switzerland consistently ranks among the world’s best countries to live and work
- Career Advancement: Multiple specialization paths and continuing education opportunities
- Permanent Residence Pathway: Healthcare professionals receive priority for long-term residence permits
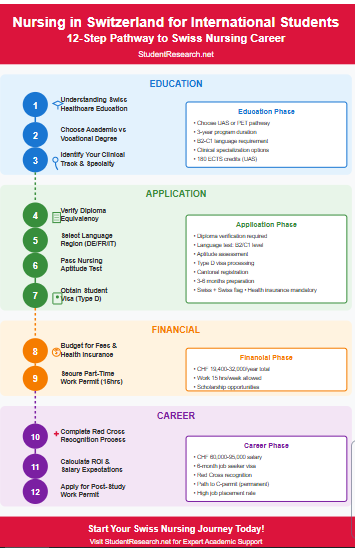
Step #1: Understanding the Global Value of a Swiss Healthcare Education
Switzerland’s healthcare system ranks among the top five globally. The country invests heavily in medical training infrastructure and research. International students gain access to cutting-edge clinical facilities and evidence-based practices that set global standards.
Benefits of the Swiss System
- Multicultural Training Environment: Work alongside diverse patient populations and international healthcare teams
- Advanced Medical Technology: Learn on state-of-the-art equipment used in leading hospitals worldwide
- Holistic Care Approach: Master patient-centered care models that integrate physical and mental health
- Trilingual Healthcare Exposure: Develop skills in German, French, or Italian medical terminology
- Research Opportunities: Participate in clinical studies at world-renowned medical institutions
- Professional Network Building: Connect with healthcare leaders across Europe and beyond
Reasons for the Healthcare Shortage: Why Switzerland is Actively Recruiting International Talent
- Aging Population Crisis: One in five Swiss residents is over 65, increasing demand for healthcare services
- Nurse Retirement Wave: Over 40% of current nurses will retire within the next decade
- Expanded Healthcare Coverage: New health initiatives require thousands of additional qualified nurses
- Nursing Initiative Policy: Government-backed program specifically designed to attract foreign healthcare workers
- Low Domestic Training Capacity: Swiss universities cannot produce enough graduates to meet demand
- Career Exodus: Many Swiss nurses leave the profession due to burnout, creating additional vacancies
Understanding the Swiss Education System: Types of Nursing Degrees
Switzerland offers two distinct pathways for nursing education. Each pathway serves different career goals and learning styles. Understanding these options helps you choose the right program for your future.
What is a Bachelor of Science (BSc) in Nursing?
A BSc in Nursing is an academic degree awarded by Universities of Applied Sciences. The program combines theoretical knowledge with clinical practice over three years. Graduates qualify for advanced roles in hospital management, research, and specialized care units.
Step #2: Choosing Between Academic and Vocational Degrees
- Career Aspirations: Academic degrees suit those targeting leadership or research positions
- Learning Preference: Consider whether you prefer theory-heavy coursework or hands-on training
- Time Commitment: UAS programs require 180 ECTS credits over three years full-time
- Cost Difference: Academic programs typically charge higher tuition than vocational schools
- International Recognition: BSc degrees transfer more easily to other countries
- Entry Requirements: Academic pathways demand stronger language proficiency and academic records
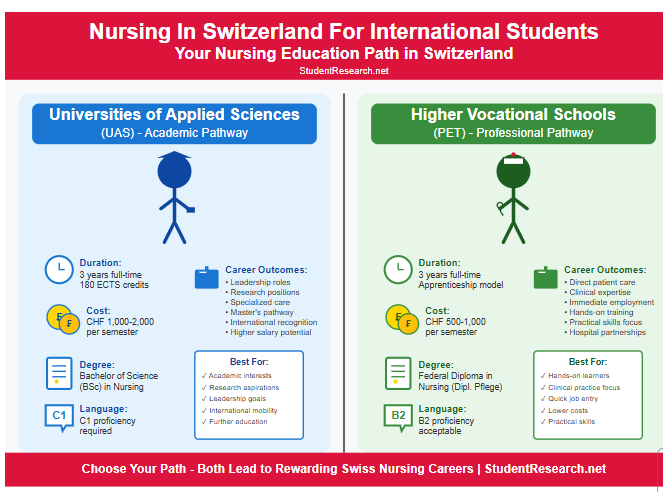
Difference Between Universities of Applied Sciences (UAS) and Higher Vocational Schools (PET)
| Universities of Applied Sciences (UAS) | Higher Vocational Schools (PET) |
|---|---|
| Academic focus with research components | Practical, workplace-oriented training |
| Awards Bachelor’s degree (BSc) | Awards Federal Diploma |
| 180 ECTS credits required | No ECTS credit system |
| Higher tuition fees (CHF 1,000-2,000/semester) | Lower costs (CHF 500-1,000/semester) |
| Pathways to Master’s programs | Direct entry to workforce |
| Requires C1 language proficiency | B2 language level acceptable |
Understanding ECTS Credits in the UAS Pathway
The European Credit Transfer System standardizes academic achievement across Europe. One ECTS credit represents 25-30 hours of student work. UAS nursing programs require 180 credits, including theoretical courses, clinical placements, and thesis work. This system allows easy transfer between European universities.
Benefits of the Practical Focus in PET Schools
- Immediate Job Readiness: Graduate with extensive hands-on clinical experience
- Industry Connections: Schools partner directly with hospitals for guaranteed placement
- Lower Language Barrier: B2 proficiency sufficient for admission and practice
- Faster Employment: Many students receive job offers before graduation
- Apprenticeship Model: Earn while you learn through paid clinical rotations
- Specialized Skills: Focus on technical nursing procedures and patient care protocols
Ways to Specialize Early in Your Education
- Choose Elective Modules: Select pediatrics, geriatrics, or psychiatric nursing courses
- Target Clinical Placements: Request rotations in your preferred specialty area
- Join Professional Associations: Network with specialists through student memberships
- Volunteer Strategically: Gain extra hours in specialized departments
- Attend Specialty Conferences: Learn from experts in your chosen field
- Complete Certification Courses: Add credentials in wound care, emergency response, or oncology
Step #3: Identifying Your Preferred Clinical Track (Pediatrics vs. Geriatrics)
Pediatric nursing focuses on treating patients from infancy through adolescence. Geriatric nursing specializes in elderly care and chronic disease management. Research both fields through hospital shadowing and informational interviews with practicing nurses. Your choice influences elective selection and clinical placement requests.
How to Apply: Steps to Meet Academic and Legal Admission Requirements
Applying to Swiss nursing programs requires careful preparation and documentation. International students must satisfy both academic qualifications and legal residence requirements.
Guide to Academic Eligibility for Foreign Students
Swiss institutions evaluate foreign credentials through swissuniversities, the national admissions body. Your high school diploma must be equivalent to the Swiss Matura certificate. Some countries require additional entrance exams or bridging courses. Universities assess each application individually based on your country’s education system.
Step #4: Verifying Your High School Diploma Equivalency
Visit the swissuniversities website to check if your diploma qualifies for direct admission. Submit certified translations of all academic documents. Some applicants must complete a one-year preparatory course before starting the nursing program. Contact your chosen institution’s admissions office for specific requirements from your country.
Understanding Language Proficiency: The B2/C1 Requirement
Language skills are crucial for patient safety and academic success. UAS programs typically require C1 level in the language of instruction. PET schools may accept B2 proficiency. You must provide official test certificates like DELF/DALF for French, Goethe-Zertifikat for German, or CILS for Italian.
Worried About Plagiarism in Your Nursing Assignments?
StudentResearch.net guarantees 100% originality on every paper. Each assignment is written from scratch and verified by industry-leading plagiarism detection software. Your academic integrity is our priority—always authentic, never copied.
Step #5: Selecting Your Language Region (German, French, or Italian)
German-speaking cantons offer the most nursing programs, including Zurich, Bern, and Basel. French is spoken in Geneva, Lausanne, and Fribourg. Italian programs exist primarily in Ticino. Consider your current language skills and regional job market when choosing. Many international students find French-speaking regions more accessible initially.
How to Pass the Swiss Nursing Aptitude Test
Many institutions require aptitude assessments to evaluate your suitability for nursing. Tests measure cognitive abilities, emotional intelligence, and stress management. Some schools include practical simulations of patient care scenarios. Preparation courses are available online and through private tutoring services.
Step #6: Preparing for Cognitive and Social Competency Assessments
Cognitive tests assess logical reasoning, numerical ability, and verbal comprehension. Social competency evaluations measure empathy, communication skills, and teamwork orientation. Practice sample questions available on university websites. Consider taking a preparatory course three to six months before your test date.
Steps to Obtain a Student Visa (Type D)
Non-EU/EFTA students need a Type D long-stay visa for studies exceeding 90 days. Apply at the Swiss embassy in your home country at least three months before your program starts. Required documents include admission confirmation, proof of financial means, health insurance, and accommodation confirmation.
Step #7: Navigating the Cantonal Migration Office Requirements
Each canton manages its own student residence permits. After arriving in Switzerland, register with the cantonal migration office within 14 days. You’ll need to present your visa, enrollment certificate, housing contract, and health insurance policy. The residence permit costs approximately CHF 150-300 annually and must be renewed each year.
Financial Planning: Benefits of Scholarships and Living Cost Statistics
Studying nursing in Switzerland requires substantial financial planning. Understanding all costs helps you budget effectively. Several funding options exist to support international students throughout their studies.
Understanding Tuition Fees for International Students
UAS tuition ranges from CHF 1,000 to CHF 2,000 per semester for international students. PET schools charge lower fees, typically CHF 500 to CHF 1,000 per semester. Additional costs include registration fees, textbooks, and mandatory health insurance. Some institutions charge differential rates for non-EU students.
Need Expert Help With Your Healthcare Essays?
StudentResearch.net employs PhD editors who refine every assignment to perfection. Your nursing papers aren’t just written—they’re meticulously polished by doctorate-level academics. Get quality-checked work that meets Swiss university standards and impresses your professors.
Step #8: Budgeting for Semester Fees and Health Insurance
Create a comprehensive budget before applying. Health insurance is mandatory and costs CHF 300-400 monthly for students. Factor in visa fees, residence permit costs, and university administrative charges.
Sample Annual Student Budget:
- • Tuition (2 semesters): CHF 2,000 – 4,000
- • Health Insurance: CHF 3,600 – 4,800
- • Accommodation: CHF 6,000 – 12,000
- • Food & Groceries: CHF 3,600 – 4,800
- • Transportation: CHF 1,200 – 1,800
- • Books & Materials: CHF 600 – 1,000
- • Personal Expenses: CHF 2,400 – 3,600
- Total Annual Budget: CHF 19,400 – 32,000
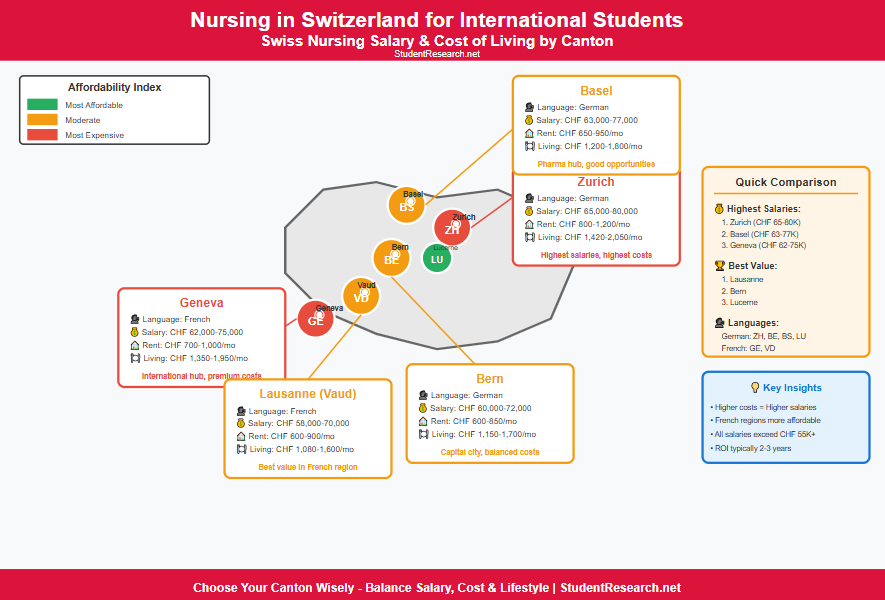
Examples of Living Expenses in Major Swiss Cities
- Zurich: Highest costs with rent averaging CHF 800-1,200 for student rooms
- Geneva: Second most expensive at CHF 700-1,000 monthly for accommodation
- Lausanne: More affordable at CHF 600-900 for student housing
- Bern: Mid-range costs with rooms at CHF 600-850 per month
- Lucerne: Similar to Bern with slightly lower food costs
- Basel: Competitive housing market at CHF 650-950 monthly
Average Costs in Zurich vs. Lausanne
| Expense Category | Zurich (CHF/month) | Lausanne (CHF/month) |
|---|---|---|
| Student Room Rent | 800 – 1,200 | 600 – 900 |
| Groceries | 300 – 400 | 250 – 350 |
| Public Transport | 70 – 100 | 50 – 80 |
| Utilities (if separate) | 100 – 150 | 80 – 120 |
| Entertainment | 150 – 200 | 100 – 150 |
| Total (excluding insurance) | 1,420 – 2,050 | 1,080 – 1,600 |
How to Work While Studying: The 15-Hour Rule
International students can work up to 15 hours per week during semesters. During semester breaks, full-time work is permitted. Many nursing students find part-time positions in healthcare facilities. This provides both income and valuable practical experience.
Step #9: Securing a Part-Time Student Permit for Non-EU Citizens
Your student residence permit automatically includes work authorization. Employers must verify your student status with the cantonal migration office. Priority goes to Swiss and EU workers, so healthcare positions are easier to secure. Popular student jobs include nursing assistant roles, hospital administration, and elderly care facilities.
The Red Cross Recognition: How to Verify Foreign Qualifications
The Swiss Red Cross (SRC) oversees nursing credential recognition in Switzerland. This process validates foreign qualifications for Swiss practice. International nurses must complete this recognition to work legally after graduation.
What is the SRC Recognition Process?
The SRC evaluates foreign nursing diplomas against Swiss standards. The process takes approximately three to six months after submitting complete documentation. Recognition may be automatic, conditional, or require compensatory measures. All foreign-trained nurses must register with the SRC database.
Step #10: Initiating the Mandatory Pre-Check for Foreign Diplomas
Submit your nursing diploma, transcripts, and curriculum outline to the SRC. Include certified translations in German, French, or Italian. The pre-check identifies any gaps in your education compared to Swiss requirements. This assessment costs approximately CHF 400-800 depending on complexity.
Fixing Qualification Gaps with Compensatory Measures
If your training lacks certain competencies, the SRC prescribes compensatory measures. These may include additional coursework, supervised practice hours, or adaptation training. Most candidates complete requirements within six to twelve months. Successfully fulfilling these measures grants full practice authorization.
Understanding Clinical Placement Requirements
Compensatory clinical placements typically last three to six months. You work under supervision in a Swiss healthcare facility. The placement covers areas missing from your original training. Facilities may offer paid positions during this adaptation period.
Career Prospects: Salary Statistics and Post-Graduation Opportunities
Swiss nursing careers offer exceptional financial rewards and professional growth. The healthcare sector provides job security and advancement opportunities. Understanding salary expectations helps you plan your long-term career trajectory.
Average Nursing Salaries Explained by Canton
- Zurich: Entry-level nurses earn CHF 65,000-80,000 annually with experienced nurses reaching CHF 95,000
- Geneva: Starting salaries range from CHF 62,000-75,000 with strong progression potential
- Basel: New graduates receive CHF 63,000-77,000 with pharmaceutical industry opportunities nearby
- Bern: Salaries begin at CHF 60,000-72,000 with public sector benefits
- Vaud (Lausanne): Entry positions offer CHF 58,000-70,000 with lower living costs
- Ticino: Italian-speaking region provides CHF 55,000-68,000 for new nurses
Step #11: Calculating Your Potential ROI After Graduation
Compare your total education investment against expected earnings. Most nursing students recover their investment within two to three years of graduation. Factor in Switzerland’s high savings potential due to competitive salaries. Consider additional income from night shifts, weekend premiums, and specialization bonuses.
When to Apply for a Post-Study Work Permit
- Timing: Begin job applications three to four months before graduation
- Job Offer Required: You need confirmed employment to convert your student permit
- Employer Sponsorship: Your hiring hospital handles most permit paperwork
- Priority Processing: Healthcare positions receive expedited approval due to shortages
- Canton Differences: Each canton has unique processing times and requirements
- Preparation Time: Allow two to three months for permit processing
Step #12: Leveraging the 6-Month Job Seeker Visa Window
Upon graduation, you can apply for a six-month job seeker visa extension. This provides time to secure suitable employment without leaving Switzerland. The extension requires proof of financial means and active job searching. Most nursing graduates find positions within two to three months given the healthcare shortage.
Transitioning from Student Visa to Permanent Residence (C-Permit)
After five to ten years of continuous residence, you can apply for permanent residence. Healthcare professionals often qualify faster due to labor market importance. The C-permit provides unrestricted work rights and easier family reunification. Maintain clean legal records and demonstrate integration through language skills and community involvement.
Conclusion
Nursing in Switzerland for international students opens doors to one of the world’s most respected healthcare systems. This comprehensive guide covers the 12 essential steps from understanding Swiss education pathways through securing permanent residence. The country’s critical healthcare shortage creates unprecedented opportunities for qualified international nurses seeking high-paying, stable careers.
Your journey begins with choosing between academic and vocational programs, followed by meeting language and admission requirements. Financial planning ensures you can afford quality education while the Red Cross recognition process validates your credentials. Swiss nursing salaries ranging from CHF 60,000 to CHF 95,000 provide excellent return on your educational investment.
The path from student to practicing nurse involves careful preparation, but the rewards are substantial. Switzerland offers not just competitive compensation, but also exceptional quality of life, professional development opportunities, and pathways to permanent residence. Take the first step today by researching programs in your preferred language region and beginning the application process. As such this research wraps up Nursing in Switzerland for international students: 12 steps to high-paying careers, admission requirements, costs, and work permits explained.
Ready to start your nursing career in Switzerland? Contact admissions offices at Universities of Applied Sciences in your chosen canton, verify your diploma equivalency through swissuniversities, and begin preparing for language proficiency exams. Your future in Swiss healthcare awaits!