Table of Contents
TogglePicture this: You’re on your first clinical rotation, and your supervising nurse asks you to convert 150 pounds to kilograms for medication dosing. Your mind goes blank. Sound familiar? Mastering medical conversions isn’t just about passing exams—it’s about patient safety and professional confidence. A conversion chart for nursing students serves as your roadmap through the complex world of medical mathematics, transforming anxiety-inducing calculations into second nature. Whether you’re struggling with metric conversions, medication dosages, or IV drip rates, this comprehensive guide will equip you with seven powerful strategies to conquer every conversion challenge you’ll face in nursing school and beyond.
Tip 1: Understanding the Fundamentals of Medical Conversions
Before diving into complex calculations, you need a solid foundation in the basics of medical measurement systems. The healthcare field primarily uses the metric system, but you’ll frequently encounter situations requiring conversions between metric, household, and apothecary measurements. Understanding why nurses need multiple measurement systems and how they interconnect will make your conversion chart for nursing students infinitely more useful in real-world applications.
Why Conversion Accuracy Matters in Patient Care
Patient safety depends entirely on precise medication administration and accurate vital sign interpretation. A single decimal point error in medication conversion can result in a tenfold overdose or underdose, potentially causing serious harm or treatment failure. Student research consistently shows that medication errors related to miscalculations remain among the top preventable adverse events in healthcare settings.
Critical areas where conversion errors occur:
- Medication dosage calculations
- IV fluid administration rates
- Pediatric weight-based dosing
- Insulin administration
The Three Main Measurement Systems Nurses Use
Understanding the relationship between different measurement systems forms the cornerstone of accurate conversions. Each system has specific applications in healthcare, and your conversion chart for nursing students should clearly distinguish between them.
Metric System (Primary):
- Based on units of 10
- Uses grams, liters, and meters
- Standard for medication administration
- Most commonly used in healthcare globally
Household System (Secondary):
- Includes teaspoons, tablespoons, and cups
- Used for patient education
- Common in home healthcare settings
- Requires careful conversion to metric
Apothecary System (Historical):
- Older measurement system
- Still appears in some medications
- Uses grains, drams, and minims
- Being phased out but appears on NCLEX
Tip 2: Building Your Essential Conversion Chart Framework

Creating a personalized conversion chart for nursing students helps you internalize the most frequently used conversions while providing a quick reference tool. Your chart should be organized logically, visually clear, and comprehensive enough to cover all common clinical scenarios without overwhelming you with unnecessary information.
Core Weight Conversions Every Nursing Student Needs
Weight conversions form the foundation of medication dosing, particularly for pediatric and critical care patients. Student research indicates that nurses use weight-based calculations multiple times per shift, making these conversions essential to master early in your education.
Essential weight conversions:
- 1 kilogram (kg) = 2.2 pounds (lb)
- 1 pound (lb) = 16 ounces (oz)
- 1 kilogram (kg) = 1000 grams (g)
- 1 gram (g) = 1000 milligrams (mg)
Quick calculation method:
- Pounds to kilograms: Divide by 2.2
- Kilograms to pounds: Multiply by 2.2
- Use 2.2 as your constant conversion factor
- Always round to nearest tenth for accuracy
Volume Measurement Conversions for Medication Administration
Volume conversions appear constantly in nursing practice, from oral medications to IV fluids. Your conversion chart for nursing students must include both metric and household volume equivalents since you’ll educate patients using familiar measurements while documenting in metric units.
Critical volume conversions:
- 1 liter (L) = 1000 milliliters (mL)
- 1 milliliter (mL) = 1 cubic centimeter (cc)
- 1 tablespoon (tbsp) = 15 mL
- 1 teaspoon (tsp) = 5 mL
- 1 fluid ounce (fl oz) = 30 mL
- 1 cup = 240 mL
Length and Height Conversions for Assessment
Accurate height measurements ensure proper body surface area calculations and growth chart plotting for pediatric patients. These conversions support nutritional assessments and dosing calculations across all patient populations.
Key length conversions:
- 1 inch (in) = 2.54 centimeters (cm)
- 1 foot (ft) = 30.48 centimeters (cm)
- 1 meter (m) = 100 centimeters (cm)
- 1 meter (m) = 39.37 inches (in)
Tip 3: Mastering Medication Dosage Calculations
Medication calculations represent the most critical application of your conversion chart for nursing students, directly impacting patient outcomes with every administration. Beyond simple conversions, you’ll combine multiple conversion steps with dosage formulas to determine exact medication amounts for diverse patient populations and clinical scenarios.
The Universal Dosage Calculation Formula
Every medication calculation follows a fundamental formula that provides consistency and accuracy across all medication types. Understanding this formula transforms your conversion chart for nursing students from a reference tool into an active calculation system.
Basic dosage formula components:
- Desired dose (what you want to give)
- Available dose (what you have on hand)
- Quantity (form the medication comes in)
- Formula: (Desired ÷ Available) × Quantity = Amount to administer
Step-by-step calculation process:
- Identify what dose is ordered
- Determine what concentration you have available
- Convert units if they don’t match
- Apply the dosage formula
- Double-check your math and units
Common Medication Concentration Conversions
Understanding medication concentrations and their conversions prevents dosing errors and ensures you can work with any medication form. Your conversion chart for nursing students should include standard concentrations for frequently administered drugs.
Standard concentration formats:
- Milligrams per milliliter (mg/mL)
- Micrograms per milliliter (mcg/mL)
- Units per milliliter (units/mL)
- Percentage solutions (%)
Percentage solution conversions:
- 1% solution = 1 gram per 100 mL
- 0.9% normal saline = 0.9 g per 100 mL
- 5% dextrose = 5 g per 100 mL
- Used extensively in IV solutions
Tip 4: Calculating IV Drip Rates and Flow Rates
Intravenous therapy calculations combine volume conversions with time calculations, requiring multiple steps and careful attention to detail. Your conversion chart for nursing students needs dedicated sections for IV calculations since they’re used continuously in hospital settings and appear heavily on nursing exams.
Understanding Drop Factors and Flow Rates
Drop factors vary by IV tubing type, and understanding this variation ensures accurate fluid administration. Student research demonstrates that IV calculation errors frequently stem from confusion about drop factors and their relationship to flow rates.
Standard drop factors by tubing type:
- Macrodrip tubing: 10, 15, or 20 drops/mL
- Microdrip tubing: 60 drops/mL
- Blood tubing: 10 drops/mL
- Pediatric tubing: 60 drops/mL (microdrip)
IV flow rate formula:
- (Volume in mL × Drop factor) ÷ Time in minutes = Drops per minute
- Always verify drop factor on tubing package
- Electronic pumps calculate in mL/hour
- Manual calculations require drops per minute
Converting Between mL/Hour and Drops/Minute
Modern IV pumps use milliliters per hour, but you’ll still calculate drops per minute for gravity infusions and need to convert between these measurements. This conversion appears frequently on the NCLEX and in clinical settings without electronic pumps.
Quick conversion methods:
- For microdrip (60 gtts/mL): mL/hour = drops/minute
- For macrodrip: Use the formula or memorize common conversions
- 100 mL/hour with 15 gtts/mL = 25 drops/minute
- Practice with various drop factors until automatic
Tip 5: Using Dimensional Analysis as Your Secret Weapon
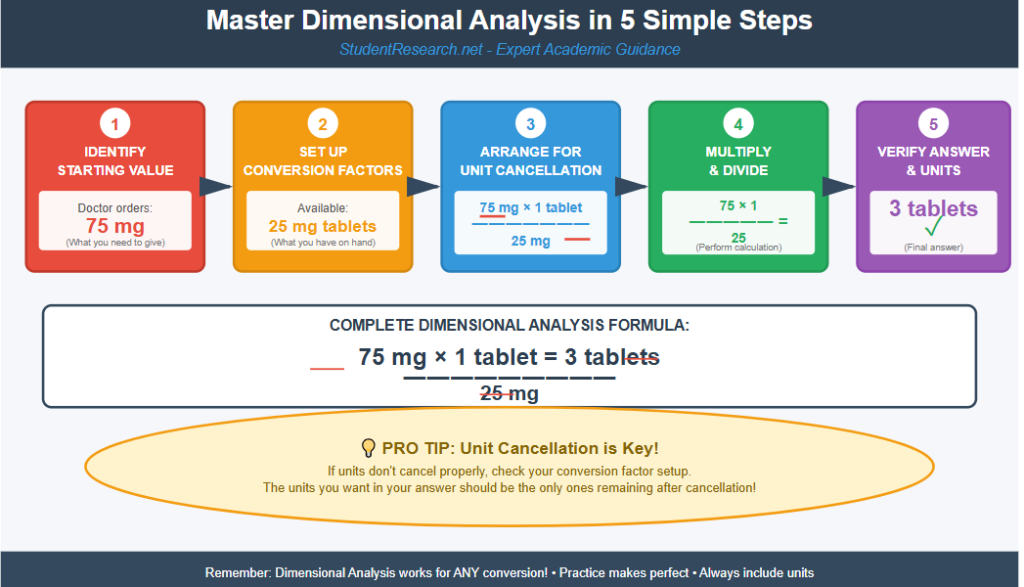
Dimensional analysis offers a systematic approach to any conversion problem, eliminating the need to memorize multiple formulas. This method, incorporated into your conversion chart for nursing students, provides a foolproof way to tackle even the most complex multi-step conversions.
Setting Up Dimensional Analysis Correctly
The beauty of dimensional analysis lies in its consistency—the same method works for every conversion type. Setting up your conversion factors correctly ensures units cancel properly and your answer has the correct units.
Dimensional analysis setup steps:
- Write the starting value with its units
- Set up conversion factors as fractions
- Arrange factors so unwanted units cancel
- Multiply across the top, multiply across the bottom
- Divide to get your final answer
Example setup structure:
- Start: 150 lb × (1 kg / 2.2 lb) = 68.2 kg
- Units cancel: pounds cancel, leaving kilograms
- Always include units in every step
- Circle your final answer with correct units
Applying Dimensional Analysis to Complex Conversions
Multi-step conversions become manageable when you string together conversion factors systematically. Your conversion chart for nursing students should include common conversion factors that you can chain together for dimensional analysis.
Complex conversion example:
- Order: 500 mg PO now
- Available: 0.25 g tablets
- Solve: 500 mg × (1 g / 1000 mg) × (1 tablet / 0.25 g) = 2 tablets
Benefits of dimensional analysis:
- Works for any conversion type
- Self-checking (units must cancel correctly)
- Reduces formula memorization
- Widely accepted in healthcare education
Tip 6: Creating Study Tools and Practice Strategies
Mastering your conversion chart for nursing students requires active practice and strategic study approaches beyond passive memorization. Developing personalized study tools and consistent practice routines transforms theoretical knowledge into clinical competence.
Struggling to Start Your Nursing Paper? StudentResearch.net provides expertly crafted foundations that help you discover your unique academic voice. Our professional writers give you the framework to confidently express complex medical concepts while maintaining your authentic style and perspective.
Flashcard Systems for Rapid Recall
Flashcards provide active recall practice, strengthening neural pathways for quick conversions under pressure. Digital or physical flashcards should cover conversions, formulas, and worked examples from your conversion chart for nursing students.
Effective flashcard categories:
- Basic metric conversions
- Household to metric equivalents
- Medication calculation formulas
- IV drip rate calculations
- Pediatric weight-based dosing
Spaced repetition strategy:
- Review new cards daily
- Review mastered cards weekly
- Focus on missed conversions
- Include worked example problems
Real-World Practice Scenarios
Applying conversions to realistic clinical scenarios bridges the gap between textbook knowledge and bedside practice. Creating practice scenarios based on actual nursing situations helps you understand when and why specific conversions are needed.
Practice scenario elements:
- Patient weight and vital signs
- Medication orders with multiple conversions
- Time-based calculations
- Error identification exercises
Sample practice problem:
- Patient weighs 176 lb, needs 5 mg/kg IV medication
- Convert: 176 lb ÷ 2.2 = 80 kg
- Calculate: 80 kg × 5 mg/kg = 400 mg dose
- Available: 200 mg/10 mL vials
- Give: (400 mg ÷ 200 mg) × 10 mL = 20 mL
Tip 7: Leveraging Technology and Digital Resources
Modern nursing students have unprecedented access to digital tools that complement traditional conversion charts. Strategic use of technology enhances accuracy, provides instant verification, and supports learning without replacing fundamental understanding of your conversion chart for nursing students.
Recommended Apps and Online Calculators
While you must perform calculations manually during exams and often in clinical settings, technology provides valuable practice tools and learning resources. The key is using these tools to reinforce understanding rather than replace learning.
Useful digital resources:
- MedCalc for medication calculations
- Nursing Central for drug information
- Quizlet for conversion flashcards
- Khan Academy for foundational math review
Best practices for technology use:
- Always work problems manually first
- Use apps to verify your calculations
- Don’t rely on technology during exams
- Understand the “why” behind each conversion
Comparative Analysis of Conversion Methods
Understanding when to use different conversion approaches optimizes your efficiency and accuracy across various clinical situations. This comparison table helps you select the most appropriate method based on the scenario.
| Conversion Method | Best Used For | Accuracy Level | Speed | Complexity | NCLEX Friendly |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Analysis | Multi-step conversions, any calculation type | Very High | Medium | Moderate | Yes – Highly Recommended |
| Ratio-Proportion | Simple conversions, familiar relationships | High | Fast | Low | Yes |
| Formula Method | Medication dosages, standard calculations | High | Medium | Moderate | Yes |
| Mental Math | Basic conversions, quick estimations | Medium | Very Fast | Low | Limited Use |
| Calculator/App | Verification, complex calculations | Very High | Very Fast | Low | No – Not Permitted |
Choosing the right method considerations:
- Exam setting: Use dimensional analysis or formula method
- Clinical setting: Use most efficient method, verify if unsure
- Learning phase: Practice all methods for flexibility
- Time pressure: Use method you’re most confident with
Building Error-Prevention Habits
Systematic error-checking procedures protect patient safety and improve your calculation confidence. Integrating these habits while using your conversion chart for nursing students prevents the most common medication errors.
Essential error-prevention strategies:
- Always write out your work completely
- Circle or highlight the answer with units
- Ask “Does this answer make sense?”
- Use the opposite conversion to verify
- Have a colleague verify high-risk medications
Red flags requiring double-checking:
- Dose seems unusually large or small
- Calculation requires multiple steps
- Units don’t match between order and available
- Pediatric or high-alert medications
- Any calculation causing uncertainty
Want to Transform Your Nursing GPA? StudentResearch.net delivers high-distinction papers that meet rigorous academic standards. Our specialized nursing writers understand complex medical calculations and concepts, creating exemplary work that elevates your grades while teaching you excellence in academic healthcare writing.
Conclusion
Mastering your conversion chart for nursing students transforms from an overwhelming challenge into an empowering skill set when you apply these seven strategic tips consistently. Remember that accuracy in medical calculations directly impacts patient safety, making this competency non-negotiable for every nursing professional. Start by building a solid foundation with fundamental conversions, then systematically practice medication dosages, IV calculations, and dimensional analysis until they become second nature. Create personalized study tools, leverage technology wisely, and develop error-prevention habits that will serve you throughout your entire nursing career.
Success with medical conversions isn’t about being naturally gifted at math—it’s about dedicated practice, systematic approaches, and refusing to cut corners when patient safety is at stake. Print your conversion chart for nursing students, keep it accessible during study sessions, and work through problems daily until conversions become automatic. The confidence you build now will translate directly into clinical competence when you’re standing at the bedside, calculator in hand, with a patient depending on your accuracy.
As you continue your nursing education journey, return to this guide whenever you need clarity on conversions or calculation methods. Share these strategies with your study group, practice together, and celebrate each milestone in your calculation competency. Your dedication to mastering these essential skills demonstrates the commitment to excellence that defines outstanding nurses. Keep practicing, stay curious, and remember that every conversion you master brings you one step closer to providing the exceptional patient care you’re called to deliver.
Meta Description: Conversion chart for nursing students made simple. Master medical calculations with 7 proven tips, practice exercises, and essential formulas for clinical success.