Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Strengths as a Student Nurse
Nursing school challenges you with rigorous coursework, demanding clinical rotations, and the emotional weight of patient care. Success requires more than technical knowledge—it demands recognizing and developing core strengths that define exceptional nurses.
What Are Strengths as a Student Nurse
- Core competencies – Technical skills and clinical knowledge you acquire through education
- Personal qualities – Empathy, resilience, and communication abilities that shape patient interactions
- Clinical abilities – Critical thinking, attention to detail, and evidence-based decision-making
- Professional attributes – Accountability, ethical practice, and commitment to excellence
Identifying your strengths matters because self-awareness helps you navigate nursing education effectively, build on natural abilities, and develop a strong professional identity.
Why Strengths as a Student Nurse Are Important
Developing your strengths creates direct pathways to career success and fulfillment:
- Enhanced Patient Outcomes – Better care quality, safety, and satisfaction
- Career Advancement – Competitive positions and leadership opportunities
- Professional Confidence – Stronger decision-making and advocacy skills
- Burnout Prevention – Improved stress management and work-life balance
- Effective Teamwork – Stronger collaboration with healthcare professionals
- Lifelong Learning – Foundation for continuous professional growth
- Patient Trust – Therapeutic relationships through competence and compassion
Reader Connection
Every nursing student experiences doubt and exhaustion. These challenges reveal opportunities to strengthen the qualities that make you exceptional. Let’s build your foundation for nursing excellence.
Clinical and Technical Strengths
Clinical and technical strengths form the foundation of safe, effective patient care. These competencies distinguish capable student nurses who deliver evidence-based care with confidence.
Quality #1: Clinical Competence and How to Develop it as a Student Nurse
Building clinical competence requires consistent practice and deliberate skill development in healthcare settings.
Steps to Continuous Practice and Skill Improvement:
Practice in simulation labs weekly – Reinforce procedures before rotations
Seek diverse patient assignments – Gain experience across different conditions
Request immediate feedback – Ask instructors to observe your technique
Review skills after shifts – Reflect on successes and improvement areas
Shadow experienced nurses – Learn efficient workflows from skilled practitioners
Ways to Improve Critical Thinking in Clinical Settings
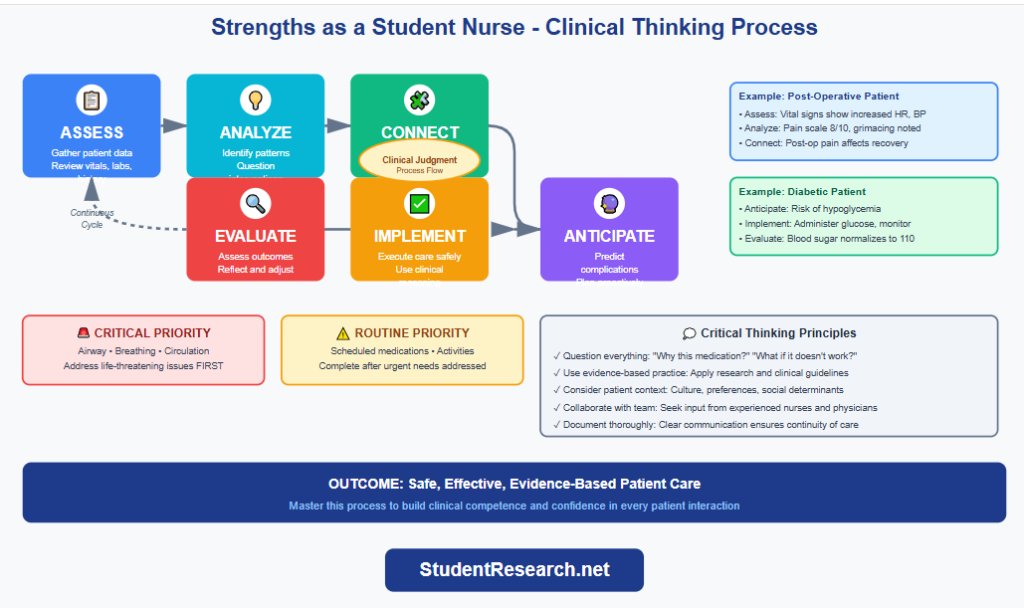
- Analyze patient data systematically – Review vitals, labs, and assessments before conclusions
- Question every intervention – Ask “why this medication?” and “what outcomes expected?”
- Connect theory to practice – Apply pathophysiology knowledge to patient scenarios
- Anticipate complications – Consider potential risks with each condition
- Use clinical reasoning frameworks – Apply SBAR or nursing process for organized thinking
What Does Attention to Detail Mean in Nursing
- Medication accuracy – Triple-check patient identity, drug, dose, route, timing
- Vital signs precision – Record measurements accurately, recognize abnormal trends
- Thorough documentation – Complete charting with specific, objective observations
Why Attention to Detail Prevents Medical Errors:
- Catches medication discrepancies before administration
- Identifies early warning signs of deterioration
- Ensures care continuity through accurate communication
Nursing pharmacology and pathophysiology overwhelming you?
StudentResearch.net simplifies complex subjects across 50+ challenging fields, including Advanced Nursing Practice, Clinical Research, Healthcare Policy, and Medical Ethics. Our experts transform complicated concepts into clear, high-quality academic work. Get specialized support for your toughest nursing courses today.
Quality #2: Adaptability Skills for Student Nurses
Healthcare demands flexibility as you encounter different units, populations, and challenges.
- Adjust to clinical specialties – Transition between medical-surgical, pediatrics, critical care settings
- Learn protocols quickly – Master different charting systems and equipment
How to Embrace Technology in Healthcare Settings
- Master electronic health records – Learn navigation shortcuts and documentation practices
- Operate medical equipment confidently – Request training on IV pumps and monitoring devices
- Understand telehealth capabilities – Familiarize with virtual monitoring and remote consultations
Interpersonal and Communication Strengths
Strong interpersonal and communication skills enable you to build therapeutic relationships and collaborate effectively within healthcare teams.
Quality #3: Compassionate Care- A Definition
Compassionate care combines clinical expertise with genuine empathy to support patients during vulnerable moments.
- Demonstrate empathy authentically – Acknowledge patient emotions without dismissing concerns
- Build trust through consistency – Follow through on promises and maintain reliable presence
- Provide emotional support – Offer reassurance during difficult diagnoses and procedures
- Respect patient dignity – Maintain privacy and honor cultural preferences
Ways to Practice Active Listening Skills in Nursing
- Focus completely on the patient – Eliminate distractions, make eye contact, and give undivided attention
- Listen beyond words – Observe body language, tone, and what patients avoid saying
- Validate patient concerns – Reflect feelings back: “It sounds like you’re worried about…”
- Ask clarifying questions – Ensure you understand patient needs before responding
- Practice cultural sensitivity – Recognize communication differences across diverse populations
Quality #4: Team Collaboration and How to Collaborate Effectively with Healthcare Teams
Effective collaboration requires respecting diverse expertise and communicating clearly with multidisciplinary professionals.
- Value all team perspectives – Recognize contributions from physicians, therapists, technicians, and support staff
- Communicate respectfully – Use professional language regardless of hierarchy or stress levels
- Share information proactively – Keep team members informed of patient changes immediately
Examples of Professional Communication in Nursing
- Structured handoff reports – Use SBAR format for clear, complete shift-to-shift communication
- Assertive physician communication – Present concerns confidently with supporting data and specific requests
- Conflict resolution skills – Address disagreements directly and professionally, focusing on patient safety
- Timely documentation – Record interventions immediately to ensure accurate care coordination
Quality #5: Patient Advocacy -Understanding Patient Advocacy as a Student Nurse
Patient advocacy means speaking up for patient needs, rights, and preferences even when challenging.
- Voice patient concerns – Communicate patient worries to physicians and care teams
- Ensure informed consent – Verify patients understand procedures before signing
- Challenge unsafe practices – Report medication errors or protocol violations immediately
- Support patient autonomy – Respect treatment decisions even when disagreeing personally
Personal and Professional Strengths
Personal and professional strengths sustain your wellbeing and uphold nursing standards throughout your career.
Quality #6: Resilience and Stress Management-How to Build Resilience and Manage Stress in Nursing School
Resilience helps you navigate emotional challenges while maintaining mental health during demanding rotations.
Coping Strategies for Emotional Challenges of Patient Care:
- Establish boundaries – Separate work emotions from personal life to prevent compassion fatigue
- Practice self-compassion – Acknowledge difficult days without harsh self-judgment
- Seek peer support – Debrief with classmates who understand nursing school pressures
- Use stress-reduction techniques – Try deep breathing, meditation, or physical exercise
- Access counseling services – Utilize campus mental health resources when overwhelmed
Ways to Improve Time Management and Organization
- Prioritize urgent tasks – Address critical patient needs before routine activities
- Create daily schedules – Block time for study, clinical prep, and self-care
- Use organizational tools – Maintain planners, apps, or checklists for assignments
Steps to Prioritizing Tasks in High-Pressure Situations:
Assess patient acuity – Identify who needs immediate attention
Follow ABC priority – Address airway, breathing, circulation first
Delegate appropriately – Ask team members for help with lower-priority tasks
Communicate delays – Inform patients if routine care must wait
Quality #7: Professionalism -What Does It Mean in Nursing Practice
Professionalism encompasses ethical behavior, maintaining boundaries, and upholding nursing standards consistently.
- Maintain strict confidentiality – Protect patient information in all settings
- Establish appropriate boundaries – Keep relationships therapeutic, not personal
- Uphold ethical standards – Follow nursing code of ethics in every situation
Examples of Accountability and Responsibility in Nursing
- Own mistakes immediately – Report errors honestly and learn from them
- Follow through on commitments – Complete promised care tasks reliably
- Recognize your limitations – Ask for help when skills exceed your competence
- Accept constructive feedback – Use criticism to improve clinical performance
Quality #8: Life-Long Learning -Why lifelong Learning Is Important for Nurses
Reasons Lifelong Learning Matters:
- Evidence-based practice evolves – New research changes best practices regularly
- Technology advances rapidly – Healthcare innovations require continuous skill updates
- Patient populations change – Demographics and health needs shift over time
- Career advancement requires it – Certifications and specializations demand ongoing education
- Patient safety depends on it – Current knowledge prevents outdated, harmful practices
How to Practice Self-Reflection as a Student Nurse
- Review clinical performance weekly – Assess what went well and needs improvement
- Set specific improvement goals – Target one skill to develop each rotation
- Seek regular feedback – Ask instructors and preceptors for honest assessments
Benefits of Embracing Constructive Criticism:
- Accelerates skill development and competence
- Prevents repeated mistakes and poor habits
- Builds professional relationships through humility
- Demonstrates commitment to excellence
Struggling to balance clinical rotations with academic papers?
StudentResearch.net crafts nursing assignments that earn you the top marks you deserve. Our nursing experts elevate your grade profile with evidence-based research, proper APA formatting, and clinically accurate content. Focus on patient care while we handle your academic excellence.
Quality #9 Integrating All Key Strengths and Developing Your Strengths as a Student Nurse
Throughout this guide, we’ve explored 10 essential strengths as a student nurse that will transform your career—from clinical skills and communication to resilience strategies that sustain you through challenges.
Key Strengths Every Student Nurse Should Develop- The 10 Essential Strengths Recap
- Clinical competence – Master hands-on patient care through deliberate practice
- Adaptability – Thrive across diverse healthcare environments and specialties
- Compassionate care – Connect with patients through authentic empathy
- Team collaboration – Work effectively with multidisciplinary professionals
- Patient advocacy – Speak up for patient needs and rights courageously
- Resilience – Manage stress and maintain mental wellbeing under pressure
- Professionalism – Uphold ethical standards and appropriate boundaries
- Lifelong learning – Embrace continuous education and evidence-based practice
- Integrated development – Recognize how these strengths interconnect and reinforce each other
- Personal planning – Create deliberate strategies for ongoing growth
These qualities don’t exist in isolation—they support and strengthen each other, creating a comprehensive foundation for nursing excellence.
Quality #10 Personal Strength Development -Steps to Identify and Build Your Nursing Strengths and Create a Personal Development Plan
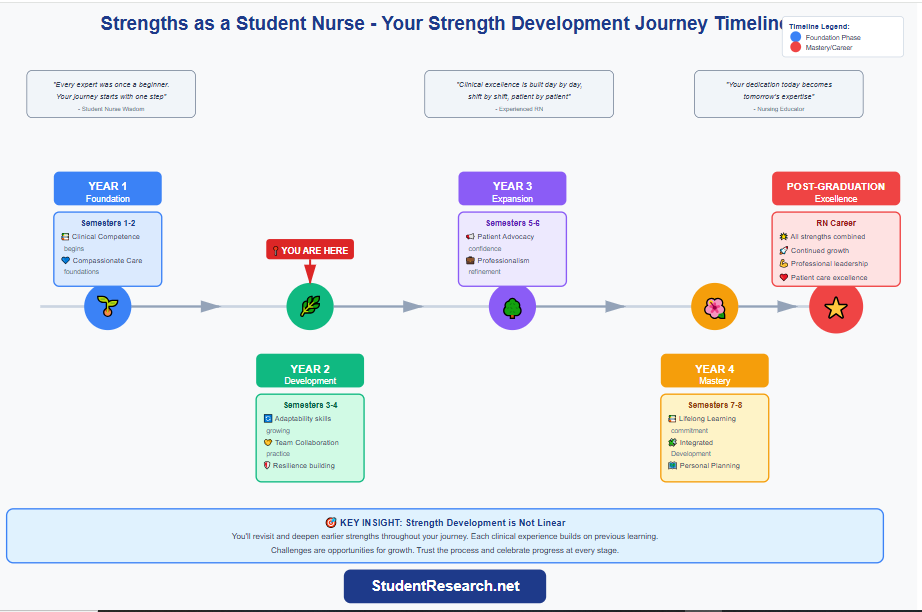
Conduct honest self-assessment – Identify current strengths and growth areas using reflection journals
Set SMART goals – Create specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, time-bound objectives for each strength
Seek diverse learning experiences – Choose clinical rotations that challenge different competencies
Request regular feedback – Ask instructors, preceptors, and peers for honest performance evaluations
Track progress systematically – Document skill improvements and celebrate milestones
Adjust plans as needed – Revise goals based on new experiences and insights
Find accountability partners – Share goals with classmates for mutual support and motivation
How to Seek Mentorship and Feedback:
- Identify experienced nurses whose strengths you admire
- Request formal mentorship or informal coffee conversations
- Ask specific questions about skill development and career paths
- Shadow mentors during clinical experiences when possible
Why Your Strengths as a Student Nurse Matter for Healthcare
- Improve patient outcomes directly – Your competence saves lives and enhances recovery
- Raise care quality standards – Excellence inspires colleagues and elevates unit performance
- Address nursing workforce needs – Well-prepared nurses reduce turnover and staffing crises
- Advance the profession – Your commitment to growth strengthens nursing’s reputation and autonomy
- Create positive ripple effects – Strong student nurses become exceptional professionals who mentor future generations
Conclusion
Your journey as a student nurse is demanding, but every challenge strengthens the qualities that will define your transformational nursing career. The 10 essential strengths you’ve explored here—clinical competence, adaptability, compassion, collaboration, advocacy, resilience, professionalism, lifelong learning, integrated development, and personal planning—form an interconnected foundation for excellence.
As you continue through nursing school, remember: you already possess incredible potential. By deliberately cultivating these strengths, seeking mentorship, and committing to continuous growth, you’re not just preparing for a job—you’re building a career that will positively impact thousands of lives. The healthcare system needs nurses like you: competent, compassionate, resilient professionals who approach patient care with both skill and heart.
Your strengths as a student nurse today become the life-saving expertise, empathetic presence, and professional leadership tomorrow’s patients desperately need. Embrace this journey, invest in your development, and trust that every step forward prepares you to deliver the exceptional care our communities deserve.